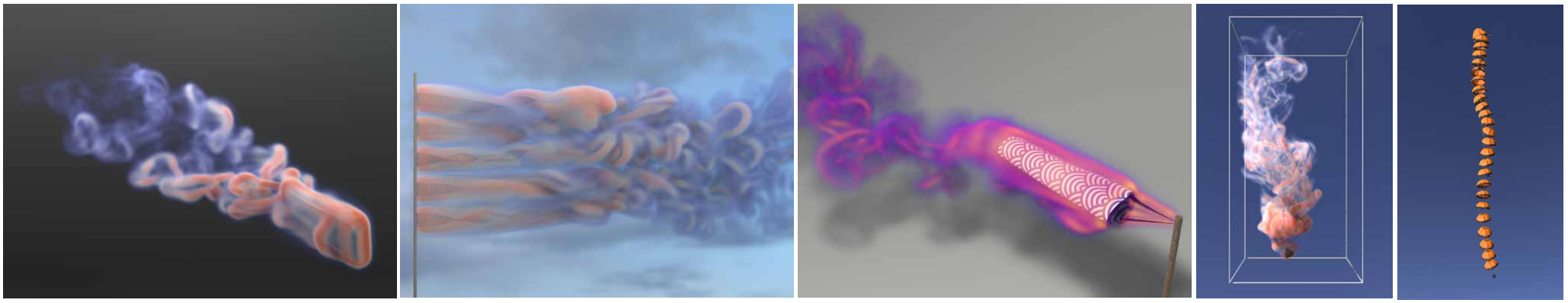
We propose a novel solid-fluid interaction method for coupling elastic solids with impulse flow maps. Our key idea is to unify the representation of fluid and solid components as particle flow maps with different lengths and dynamics. The solid-fluid coupling is enabled by implementing two novel mechanisms: first, we developed an impulse-to-velocity transfer mechanism to unify the exchanged physical quantities; second, we devised a particle path integral mechanism to accumulate coupling forces along each flow-map trajectory. Our framework integrates these two mechanisms into an Eulerian-Lagrangian impulse fluid simulator to accommodate traditional coupling models, exemplified by the Material Point Method (MPM) and Immersed Boundary Method (IBM), within a particle flow map framework. We demonstrate our method's efficacy by simulating solid-fluid interactions exhibiting strong vortical dynamics, including various vortex shedding and interaction examples across swimming, falling, breezing, and combustion.
@article{chen2024solidfluid,
title={Solid-Fluid Interaction on Particle Flow Maps},
author={Chen, Duowen and Li, Zhiqi and Zhou, Junwei and Feng, Fan and Du, Tao and Zhu, Bo},
journal={ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG)},
volume={43},
number={6},
pages={1--20},
year={2024},
publisher={ACM New York, NY, USA}
}